4、Sun Yuewu and Sun Chunlin used the characteristics of plant epidermal stomata to study the global atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration for the first time in the Middle Jurassic of Liaoning and the Early Cretaceous in Jilin. The CO2 concentration measured in the early Middle Jurassic and Early Cretaceous Aptian-Albian is the current atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. 2-4 times as much as the greenhouse climate. At the same time, based on paleontology, isotope dating, etc., the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration value is related to the early Cretaceous ocean hypoxic event, and the global oceanic hypoxic event (OAE1b) and its interval (OAE1a and OAE1b) are reconstructed. It proves that the Mesozoic greenhouse climate is closely related to the atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration. The increase in terrestrial biodiversity and the lack of oxygen in the ocean are feedbacks to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration; the above results have strongly promoted the in-depth study of the Mesozoic and Cenozoic terrestrial ecosystems in China.

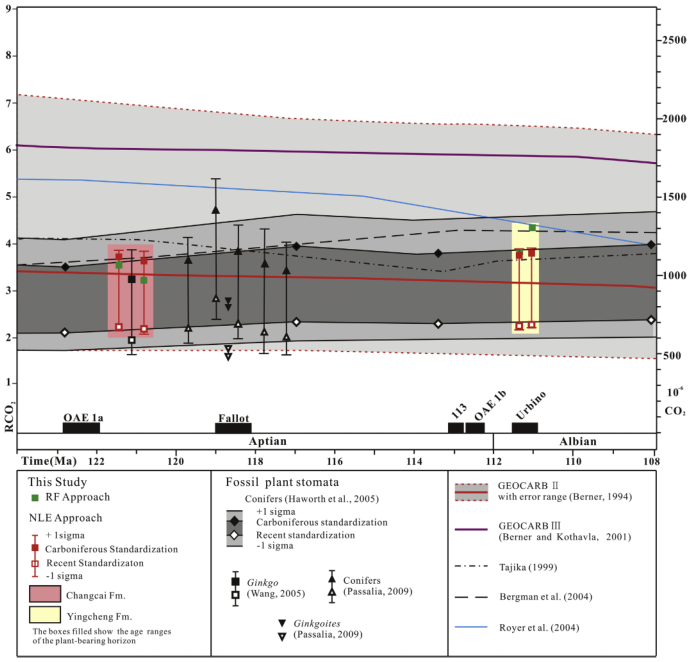
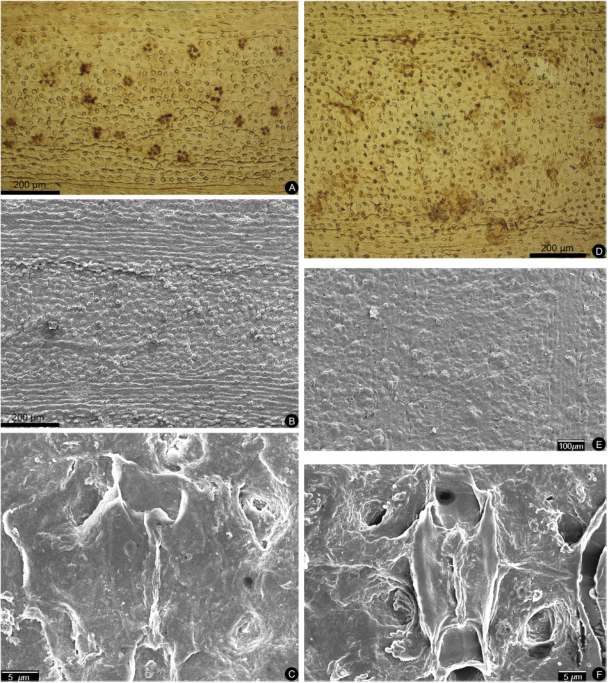
Aptian and Albian atmospheric CO2 changes on the basis of fossil Ginkgo cuticles in Jilin Province